
STRUCTURE OF LIVER
-Liver consist of many lobes.
-Two blood vessels supply blood to liver and one drains blood away from it:
>Hepatic Artery-Supply oxygenated blood to liver.
>Hepatic Portal Vein-Supply blood from intestine transporting water soluble digested nutrients to liver.
>Hepatic Vein-Drain blood away from the liver transporting deoxygenated blood back to heart.
-Branches from hepatic arteries and hepatic portal veins enter into the lobules from portal region.
-Bile canaliculi transport bile to bile ducts found in portal region.
-Bile from bile duct is later channelled to gall bladder.
-Liver cells called hepatocytes are arranged in strands radiating from central vein towards the periphery.
-Central vein collects blood away from the lobule.
-Each lobule is supplied with blood from hepatic arteriole and hepatic portal vein, which fuse to form many capillaries called sinusoids and flow to the central vein.
-Special amoeboid cells called Kupffer cells are attached to the inner wall of sinusoids for phagocytosis of old red blood cells and pathogens.
-Bile is produced in the hepatocytes and secreted into canaluculus which them empties bile into bile ducts.
-Bile is collected by the gall bladder for temporary storage before it is emptied into the duodenum.
FUNCTION OF LIVER
1.Regulates blood glucose level at 80-100mg/100ml of blood.
a)Stimulate condensation of excess glucose into glycogen which is then stored-Glycogenesis-occurs in the present of insulin.
b)Stimulate break down of glycogen into glucose in the present of glucagon-Glycogenolysis.
c)Stimulate synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate substances such as fat through Gluconeogenesis.
d)Release glucose into blood circulation if blood glucose level becomes lower than normal range.
e)Stimulates conversion of lactate (lactic acid) produced through anaerobic respiration in skeletal muscle cell into glucose. The lactate may also be broken down to produce energy lactate from skeletal muscles are transported to liver through Cori Cycle.
2.Regulates body protein level
a)Excess amino acid goes through deamination in liver to produce ammonia and keto acid.

b)Ammonia produced through deamination is converted into urea through Ornithine Cycle.
c)Synthesis of non-essential amino acid through transamination.
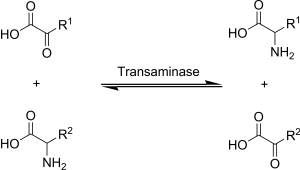
3.Regulates lipid level in body
a)Does synthesis and break down of steroids such as cholesterol.
b)Does synthesis of fat-lipogenesis
c)Break down of fat.
4.Does detoxification in which toxic substance such as alcohol are converted into non-toxic substances.
5.Synthesis of plasma protein such as prothrombin.
6.Synthesis of Red Blood cells in foetus stage.
7.Acts as reservoir of blood.
8.Stores nutrients such as vitamin A, D, B12 and minerals such as Fe2+ ions.
9.Synthesis of bile which is used for emulsification of fat in duodenum.
Cori Cycle
-Through anaerobic respiration/lactate fermentation, skeletal muscles produce lactate.
-Lactate produced in the muscles are transported to the liver by blood circulation.
-In liver, lactate may be broken down to produce energy or converted back into glucose.
-Glucose produced can be transported back to muscles or stored as glycogen.
Ornithine Cycle
-is a process involved in conversion of ammonia into urea.
-Ammonia produced through deamination is bind with CO2, H2O and phosphate group using energy to form Carbomoyl Phosphate.
-This process occurs in matrix of Mitochondrion.
-Carbomoyl phosphate binds with Ornithine and then releases phosphate group to forum Citruline.
-Citruline is transported into cytoplasm, it binds with Aspartate to form Argnininosuccinate.
-Argininosuccinatre splits to form fumerate and arginine.
-Hydrolysis of Arginine produces urea and regenerates Ornithine.
-Ornithine is transported into matrix of mitochondria and the processes are repeated.
Break down of Red Blood Cells
-Old/worn-out Red Blood Cells are destroyed by Kupffer cells in liver.
-Haemoglobin is broken in liver cells to produce Haem and Globin.
-Globin(tertiary structure protein) are hydrolysed to produce amino acids which are then reused.
-Haem is broken down to produce Porphyrin ring and Iron ion.
-Porphyrin rings are broken down and use for synthesis of bile pigments, bilirubin and biliverdin.
-Bile pigments are used in synthesis of bile.
-The Iron ions are stored in liver as Ferrifin or transported back to bone marrow as iron-transferrin complex.
No comments:
Post a Comment